-
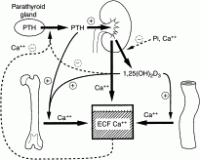
Overview of calcium homeostasis
-
Calcium distribution within the body
-
Extracellular Calcium
-
Intracellular Calcium
-
Parathyroid hormone
-
Structure
-
Synthesis and secretion
-
Set-Point for PTH Secretion
-
Inhibition of PTH Synthesis and Secretion
-
Clearance and metabolism of parathyroid hormone
-
Actions of parathyroid hormone
-
Parathyroid Hormone C-Terminal 7-84 as PTH Antagonist
-
Parathyroid Hormone Receptor
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein: a polyhormone
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein in the fetus
-
Vitamin D
-
Vitamin D metabolism
-
Synthesis
-
Actions of Calcitriol
-
The calcitriol receptor
-
Effects of Calcitriol on the Intestine
-
Effects of Calcitriol on Bone
-
Effects of Calcitriol on the Kidneys
-
Effects of Calcitriol on the Parathyroid Gland
-
Calcitriol in cancer therapy?
-
Calcitonin
-
Normal homeostatic response to hypocalcemia
-
Normal homeostatic response to hypercalcemia
-
Diagnostics
-
Total calcium
-
Analytical Methods
-
Normal Values
-
Adjusted Total Calcium
-
Ionized calcium
-
Analytical Methods
-
Sample Handling Techniques
-
Normal Values
-
Fractionation of Serum Calcium
-
Parathyroid hormone
-
Parathyroid hormone-related protein
-
Vitamin D metabolites
-
Bone biopsy and bone marrow aspiration
-
Hypercalcemia
-
Toxicity of hypercalcemia and clinical signs
-
Renal Effects of Hypercalcemia
-
Effects of Hypercalcemia on Other Organs
-
Mechanisms and differential diagnosis of hypercalcemia
-
General approach to diagnostic workup of patients with hypercalcemia
-
Nonpathologic hypercalcemia
-
Transient or Inconsequential Hypercalcemia
-
Hypoadrenocorticism
-
Chronic Renal Failure
-
Pathologic or consequential hypercalcemia
-
Cancer-Associated Hypercalcemia
-
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
-
Hypervitaminosis D
-
Granulomatous Disease
-
Idiopathic Hypercalcemia of Cats
-
Uncommon Causes of Hypercalcemia
-
Treatment of hypercalcemia
-
Philosophy of Treatment
-
Definitive Therapy
-
Supportive Therapy
-
Initial Considerations for Treatment
-
Future Considerations
-
Additional Specific Treatments for Hypervitaminosis D
-
Hypocalcemia
-
Introduction
-
Consequences of hypocalcemia and clinical signs
-
Approach to hypocalcemia
-
Differential diagnosis and mechanisms of hypocalcemia
-
Hypoalbuminemia
-
Renal Failure
-
Emergency and Critical Care
-
Small Intestinal Diseases
-
Alkali Administration
-
Acute Reversal of Chronic Hypercalcemia
-
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
-
Nutritional Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
-
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism Associated with Hyperadrenocorticism
-
Effects of drugs
-
Hypoparathyroidism
-
Miscellaneous Causes of Hypocalcemia
-
Treatment of hypocalcemia
-
Acute Management of Hypocalcemia Causing Tetany or Seizures
-
Subacute Management of Hypocalcemia
-
Subacute and Chronic Maintenance
-
Clinical follow-up and potential complications
-
References